For each compound, give the product(s) expected from (1) HgSO4/H2SO4 - catalyzed hydration and (2) hydroboration–oxidation.
b. hex-2-yne
 Verified step by step guidance
Verified step by step guidance Verified video answer for a similar problem:
Verified video answer for a similar problem: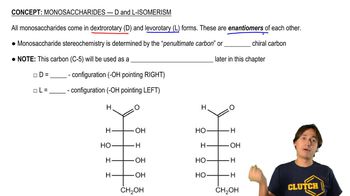
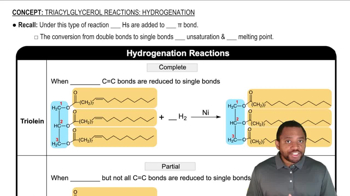


 2:43m
2:43mMaster Anti-Markovnikov addition of alcohols to terminal alkynes yields aldehydes with a bite sized video explanation from Johnny
Start learning