Show how to make these deuterium-labeled compounds, using CD3MgBr and D2O as your sources of deuterium, and any non-deuterated starting materials you wish.
c. CD3CH2CH2OH
 Verified step by step guidance
Verified step by step guidance Verified video answer for a similar problem:
Verified video answer for a similar problem: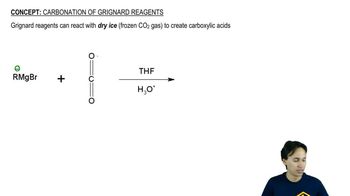
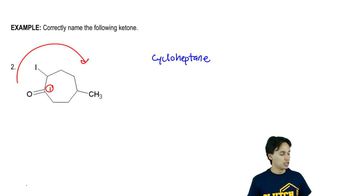

 13:4m
13:4mMaster Reactions of Organometallics with a bite sized video explanation from Johnny
Start learning