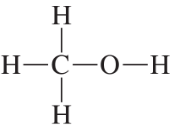
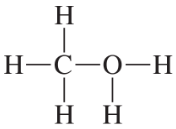
Based on the formal charge, determine how many lone pairs are on each indicated atom.
(a)
 Verified step by step guidance
Verified step by step guidance Verified video answer for a similar problem:
Verified video answer for a similar problem:


 1:34m
1:34mMaster Calculating formal and net charge. with a bite sized video explanation from Johnny
Start learning