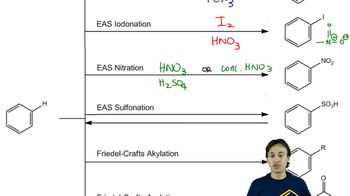
Show an arrow-pushing mechanism that forms the product on the right from the reactant at left. Only one arrow is necessary in each reaction. [Don't forget to draw in the lone pairs on this and the next two assessments.]
(d)
 Verified step by step guidance
Verified step by step guidance Verified video answer for a similar problem:
Verified video answer for a similar problem:


 5:14m
5:14mMaster How to tell if a molecule will be reactive or not. with a bite sized video explanation from Johnny
Start learning