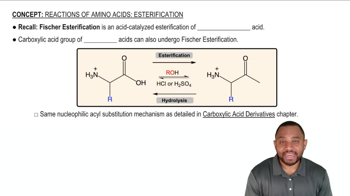
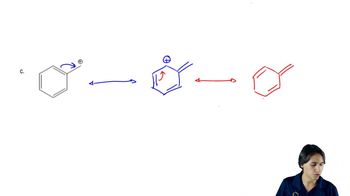
a. A student did not obtain any ester when he added 2,4,6-trimethylbenzoic acid to an acidic solution of ethanol. Why? (HINT: Build models.)
b. Would he have encountered the same problem if he had tried to synthesize the methyl ester of 4-methylbenzoic acid in the same way?