For each of the following compounds, draw the product that forms in an E2 reaction and indicate its configuration:
a. (1S,2S)-1-bromo-1,2-diphenylpropane
 Verified step by step guidance
Verified step by step guidance Verified video answer for a similar problem:
Verified video answer for a similar problem: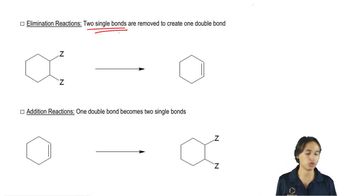


 1:18m
1:18mMaster Defining Zaitsev’s Rule with a bite sized video explanation from Johnny
Start learning