Provide a mechanism for the following SN1 reactions that feature a rearrangement.
(b)
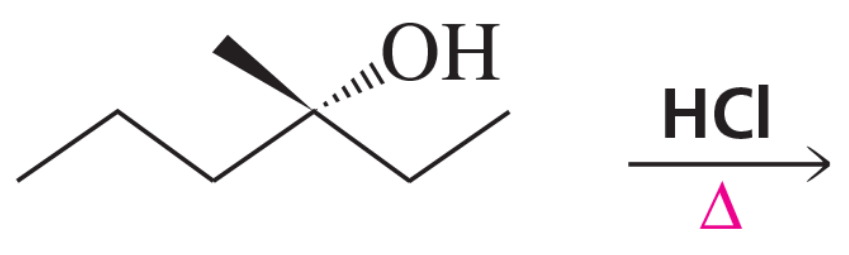
 Verified step by step guidance
Verified step by step guidance Verified video answer for a similar problem:
Verified video answer for a similar problem:


 3:32m
3:32mMaster How do we predict if the mechanism is SN1 or SN2? with a bite sized video explanation from Johnny
Start learning