What is the major product obtained when each of the following alcohols is heated in the presence of H2SO4?
a.
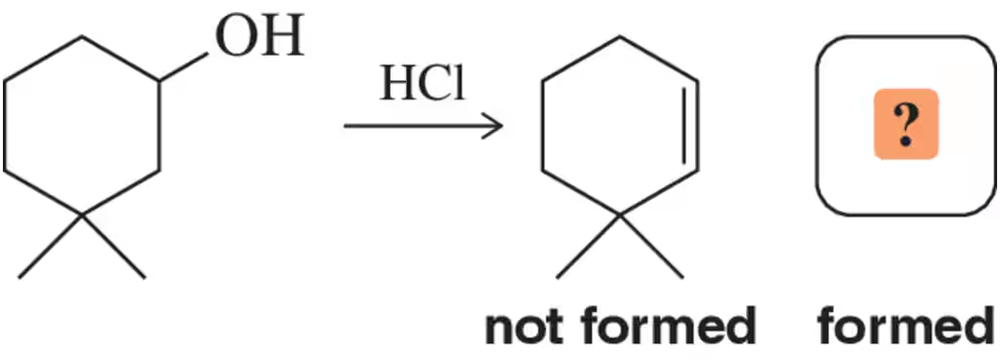
 Verified step by step guidance
Verified step by step guidance Verified video answer for a similar problem:
Verified video answer for a similar problem: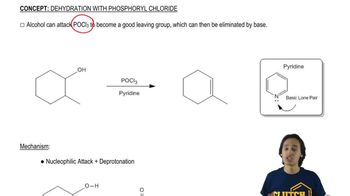

 6:01m
6:01mMaster General features of acid-catalyzed dehydration. with a bite sized video explanation from Johnny
Start learning