Predict the products formed when cyclohexanone reacts with the following reagents.
(f) PhMgBr and then mild H3O+
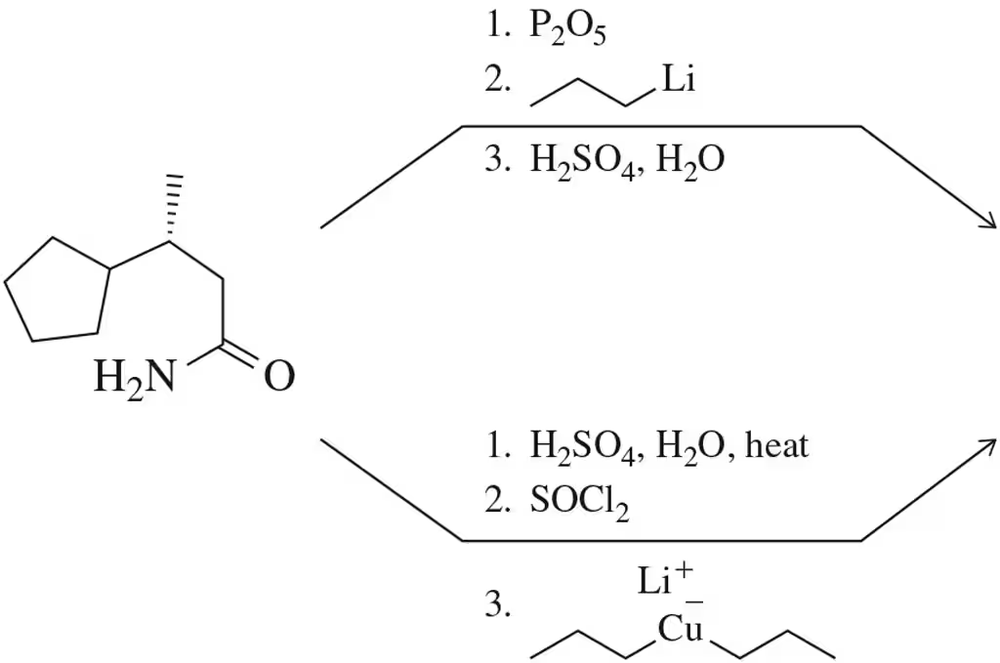
 Verified step by step guidance
Verified step by step guidance Verified video answer for a similar problem:
Verified video answer for a similar problem:



 13:4m
13:4mMaster Reactions of Organometallics with a bite sized video explanation from Johnny
Start learning