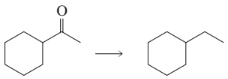
Show how you would accomplish the following synthetic conversions efficiently and in good yield. You may use any necessary additional reagents and solvents.
(b)
 Verified step by step guidance
Verified step by step guidance Verified video answer for a similar problem:
Verified video answer for a similar problem:


 2:49m
2:49mMaster Aromatic synthesis starting with benzene/benzene derivatives with a bite sized video explanation from Johnny
Start learning