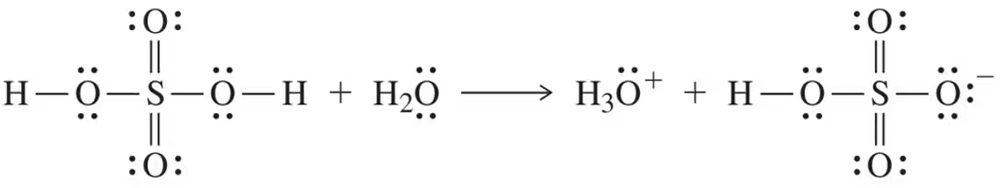Oxidation of a primary alcohol to an aldehyde usually gives some over-oxidation to the carboxylic acid. Assume you have used PCC to oxidize pentan-1-ol to pentanal.
(a) Show how you would use acid–base extraction to purify the pentanal.
(b) Which of the expected impurities cannot be removed from pentanal by acid–base extractions? How would you remove this impurity?