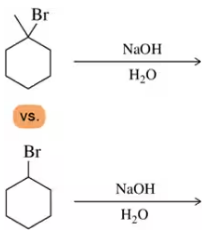
Textbook Question
For each pair, choose the haloalkane that would react most quickly in an SN1 or E1 reaction.
(b)
 Verified step by step guidance
Verified step by step guidance Verified video answer for a similar problem:
Verified video answer for a similar problem:


 7:22m
7:22mMaster The 3 important leaving groups to know. with a bite sized video explanation from Johnny
Start learning