For each of the acid–base reactions in [Section 2.3], compare the pKa values of the acids on either side of the equilibrium arrows to prove that the equilibrium lies in the direction indicated.
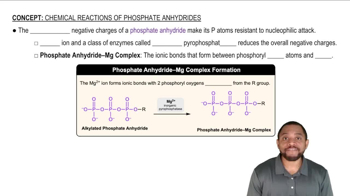
3. <IMAGE>
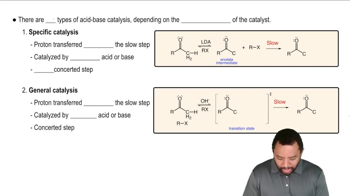
4. <IMAGE>
 Verified step by step guidance
Verified step by step guidance Verified video answer for a similar problem:
Verified video answer for a similar problem:

 5:11m
5:11mMaster The 3 steps for determining the direction of acid and base equilibrium. with a bite sized video explanation from Johnny
Start learning