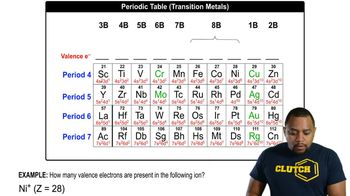
How many electrons does an atom of each of the following elements need to lose to achieve a noble gas configuration? By losing that many electrons, which noble gas configuration is achieved?
(c) Magnesium
 Verified step by step guidance
Verified step by step guidance Verified video answer for a similar problem:
Verified video answer for a similar problem:

 1:01m
1:01mMaster How Noble gases are related to the octet rule. with a bite sized video explanation from Johnny
Start learning