What monosaccharides are formed in a modified Kiliani–Fischer synthesis starting with each of the following monosaccharides?
a. D-xylose
 Verified step by step guidance
Verified step by step guidance Verified video answer for a similar problem:
Verified video answer for a similar problem: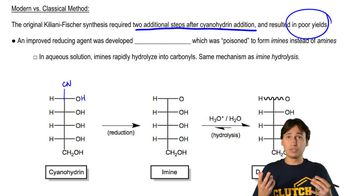
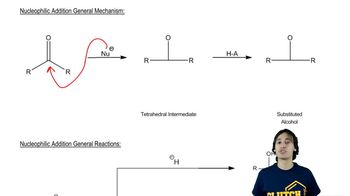
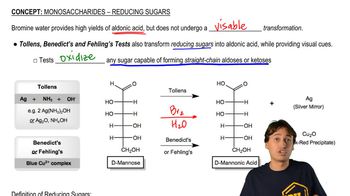

 7:50m
7:50mMaster Monosaccharides - Kiliani-Fischer with a bite sized video explanation from Johnny
Start learning