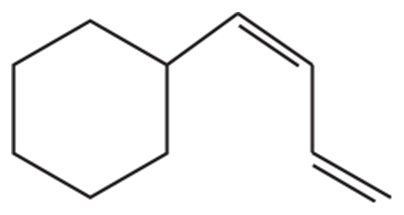
What bromo-substituted compound would be required to react with (CH2=CH)2CuLi in order to form each of the following compounds?
b.
 Verified step by step guidance
Verified step by step guidance Verified video answer for a similar problem:
Verified video answer for a similar problem:

 0:24m
0:24mMaster Intro to Predict the Product with a bite sized video explanation from Johnny
Start learning