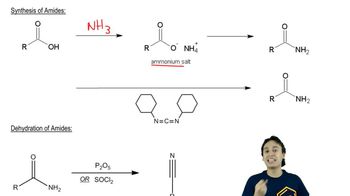
The two most general amine syntheses are the reductive amination of carbonyl compounds and the reduction of amides. Show how these techniques can be used to accomplish the following syntheses.
(c) pyrrolidine → N-ethylpyrrolidine
 Verified step by step guidance
Verified step by step guidance Verified video answer for a similar problem:
Verified video answer for a similar problem:

 9:12m
9:12mMaster The Primary Amines Flowchart with a bite sized video explanation from Johnny
Start learning