Suggest a synthetic scheme, involving a protecting group, to generate the molecule shown starting with the molecule at the left.
(b)
 Verified step by step guidance
Verified step by step guidance Verified video answer for a similar problem:
Verified video answer for a similar problem: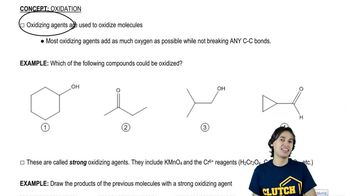
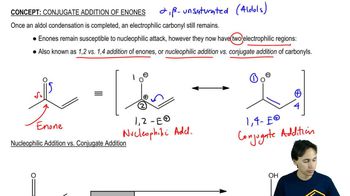
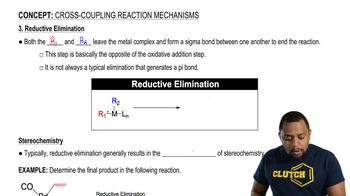

 0:24m
0:24mMaster Intro to Predict the Product with a bite sized video explanation from Johnny
Start learning