Draw the reaction-energy diagram for the following reverse reaction:
•CH3 + HCl → CH4 + Cl•
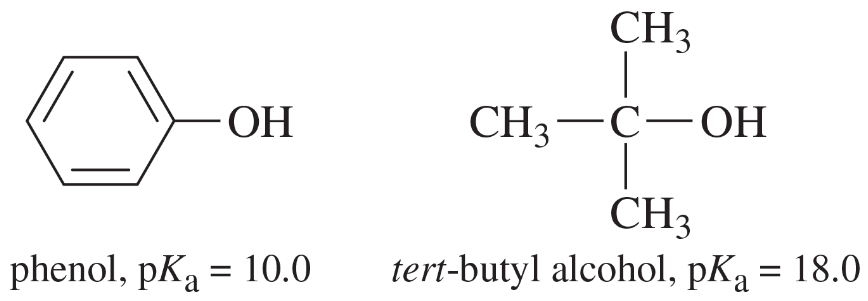
 Verified step by step guidance
Verified step by step guidance Verified video answer for a similar problem:
Verified video answer for a similar problem:

 6:07m
6:07mMaster Introduction to free energy diagrams. with a bite sized video explanation from Johnny
Start learning