Given the value of Keq for the following acid–base reactions, identify the weakest acid and the weakest base.
(c)
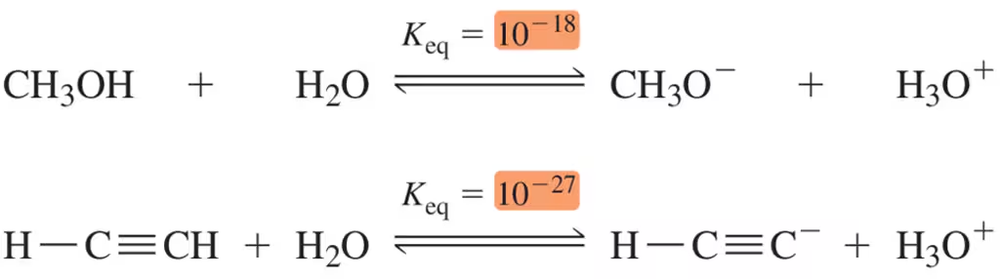
 Verified step by step guidance
Verified step by step guidance Verified video answer for a similar problem:
Verified video answer for a similar problem:



 5:11m
5:11mMaster The 3 steps for determining the direction of acid and base equilibrium. with a bite sized video explanation from Johnny
Start learning