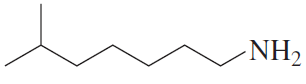
Give a systematic name and a common name (if it has one) for each of the following amines and indicate whether each is a primary, secondary, or tertiary amine:
c.
d.
 Verified step by step guidance
Verified step by step guidance Verified video answer for a similar problem:
Verified video answer for a similar problem: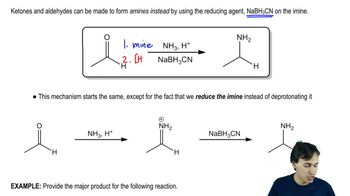

 6:50m
6:50mMaster Naming Primary Amines with a bite sized video explanation from Johnny
Start learning