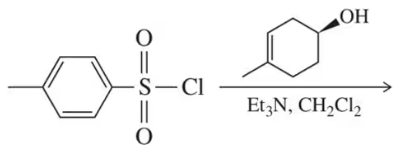
On the reaction coordinate diagram for the disfavored nucleophilic displacement of hydroxide, predict the curve that would demonstrate how using a tosylate makes the substitution favorable.
<IMAGE>
 Verified step by step guidance
Verified step by step guidance Verified video answer for a similar problem:
Verified video answer for a similar problem: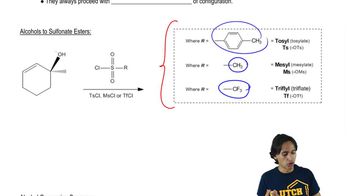


 7:53m
7:53mMaster Learning the mechanism of Sulfonyl Chlorides. with a bite sized video explanation from Johnny
Start learning