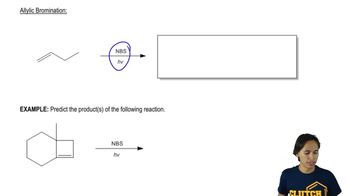
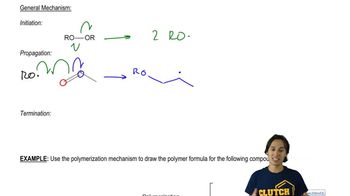
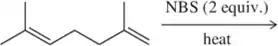
The light-initiated reaction of 2,3-dimethylbut-2-ene with N-bromosuccinimide (NBS) gives two products:
a. Give a mechanism for this reaction, showing how the two products arise as a consequence of the resonance-stabilized intermediate.
 Verified step by step guidance
Verified step by step guidance Verified video answer for a similar problem:
Verified video answer for a similar problem: