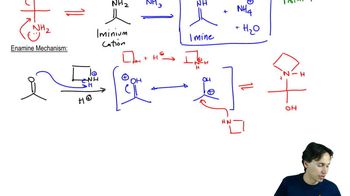
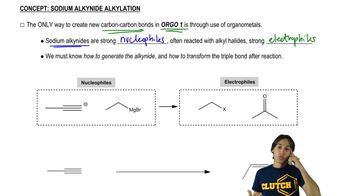
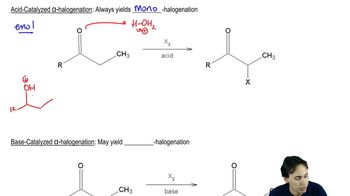
Write equations showing the expected products of the following enamine alkylation and acylation reactions. Then give the final products expected after hydrolysis of the iminium salts.
(c) piperidine enamine of cyclopentanone + methyl iodide
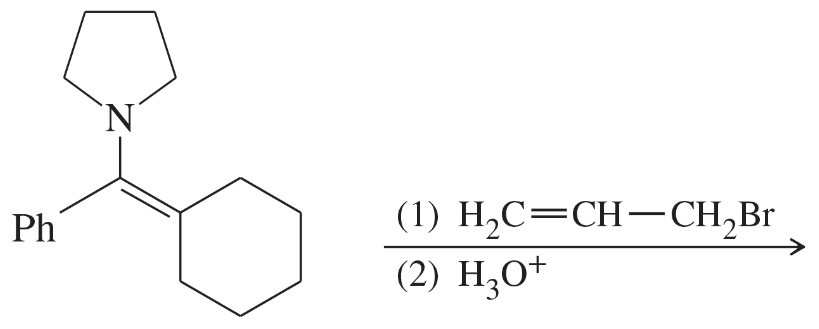
 Verified step by step guidance
Verified step by step guidance Verified video answer for a similar problem:
Verified video answer for a similar problem: