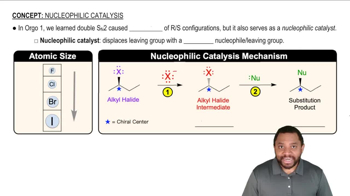
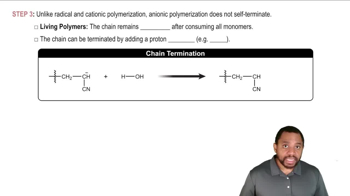
Show how you would synthesize the following compounds. As starting materials, you may use any alcohols containing four or fewer carbon atoms, cyclohexanol, and any necessary solvents and inorganic reagents.
(h)
 Verified step by step guidance
Verified step by step guidance Verified video answer for a similar problem:
Verified video answer for a similar problem: