Allylic halides have the structure
b. Draw the resonance structures of the allylic cations formed by ionization of the following halides.
(i)
(ii)
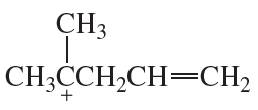
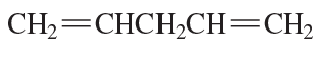
 Verified step by step guidance
Verified step by step guidance Verified video answer for a similar problem:
Verified video answer for a similar problem:
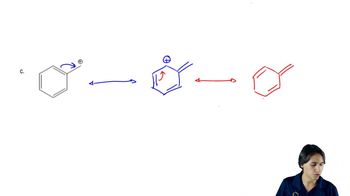
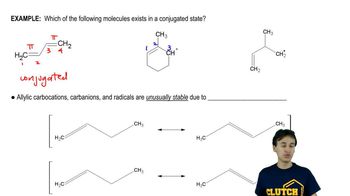

 3:34m
3:34mMaster The rules you need for resonance: with a bite sized video explanation from Johnny
Start learning