For each of the following acid–base reactions, (ii) calculate Keq. If a pKa is not one of the ten common ones we learned in Chapter 4, it will be given to you.
(a)
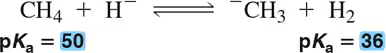
 Verified step by step guidance
Verified step by step guidance Verified video answer for a similar problem:
Verified video answer for a similar problem:



 1:46m
1:46mMaster Why we use pKa instead of pH. with a bite sized video explanation from Johnny
Start learning