Textbook Question
Draw the structure for each of the following:
h. cyclohexanecarbonyl chloride
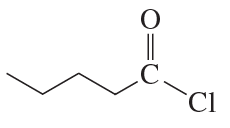
 Verified step by step guidance
Verified step by step guidance Verified video answer for a similar problem:
Verified video answer for a similar problem: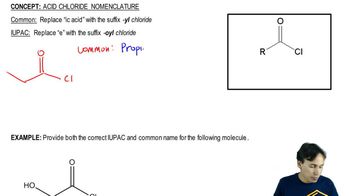


 3:13m
3:13mMaster Acid Chloride Nomenclature with a bite sized video explanation from Johnny
Start learning