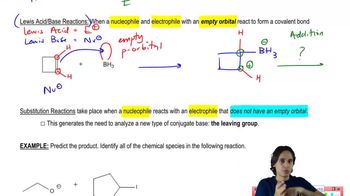
The following are all substitution reactions, two of which we study in later chapters. With no knowledge of mechanism, what would you expect the ratio of products to be for each reaction, based on a random statistical distribution?
(a) Replacing a hydrogen (H) with deuterium (D):