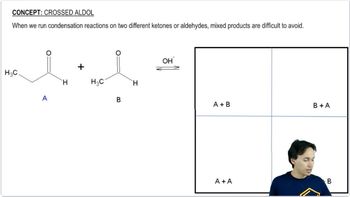
The following compounds can be synthesized by aldol condensations, followed by further reactions. (In each case, work backward from the target molecule to an aldol product, and show what compounds are needed for the condensation.)
(b)
 Verified step by step guidance
Verified step by step guidance Verified video answer for a similar problem:
Verified video answer for a similar problem: