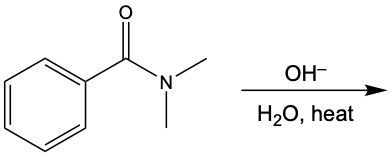
Identify the functional group in the following compounds and give the structures of the products of hydrolysis for these compounds.
a. <IMAGE>
 Verified step by step guidance
Verified step by step guidance
 1:12m
1:12mMaster Acidic Hydrolysis Concept 1 with a bite sized video explanation from Jules
Start learning
