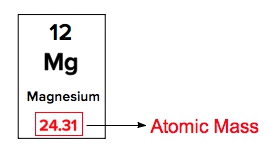
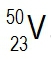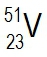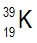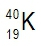Atomic masses of elements are readily available on the periodic table, where each element is represented by a symbol, such as H for hydrogen. The whole numbers associated with each element indicate their atomic number, which corresponds to the number of protons in the nucleus. In contrast, atomic mass is typically not a whole number; it represents the weighted average of all isotopes of an element.
The atomic mass is expressed in units of grams per mole, atomic mass units (AMU), or Daltons. A key relationship to remember is that 1 AMU is equivalent to \(1.66 \times 10^{-27}\) kilograms. This means that while the atomic masses listed on the periodic table are averages, they provide crucial information about the isotopic composition of the element. Generally, only the heavier elements may display whole number atomic masses, as lighter elements tend to have non-integer values due to the presence of multiple isotopes.