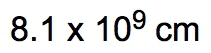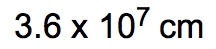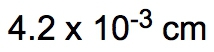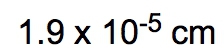Dimensional analysis is a systematic method used to convert units from one system to another, ensuring accuracy in calculations. The process begins with a known quantity, referred to as the given amount, and aims to arrive at the desired unit, known as the end amount. The key to successful dimensional analysis lies in the use of conversion factors, which are ratios that express the relationship between different units.
For instance, to convert 32 inches to centimeters, one would utilize the conversion factor that states 1 inch is equal to 2.54 centimeters. By setting up the equation with inches in the denominator, the units cancel out, allowing for a straightforward multiplication:
\[32 \, \text{inches} \times \frac{2.54 \, \text{cm}}{1 \, \text{inch}} = 81.28 \, \text{cm}\]
However, when determining significant figures, the result must reflect the least number of significant figures from the original measurements. In this case, 32 has 2 significant figures, leading to a final answer of 81 cm after rounding.
In more complex conversions, such as converting 115 minutes to years, multiple conversion factors are employed. The process involves sequentially canceling out units:
\[115 \, \text{minutes} \times \frac{1 \, \text{hour}}{60 \, \text{minutes}} \times \frac{1 \, \text{day}}{24 \, \text{hours}} \times \frac{1 \, \text{year}}{365 \, \text{days}}\]
Calculating the total for the denominator (60 minutes/hour × 24 hours/day × 365 days/year) yields 525,600. Thus, the calculation becomes:
\[\frac{115}{525600} \approx 2.19 \times 10^{-4} \, \text{years}\]
In this case, the significant figures are determined solely by the given amount, which has 3 significant figures, ensuring the final answer maintains this precision.
Overall, dimensional analysis is a powerful tool that relies on the careful application of conversion factors to facilitate unit conversion while maintaining accuracy through significant figures. Mastery of this technique is essential for effective problem-solving in various scientific and mathematical contexts.