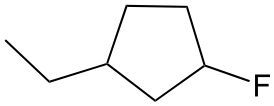
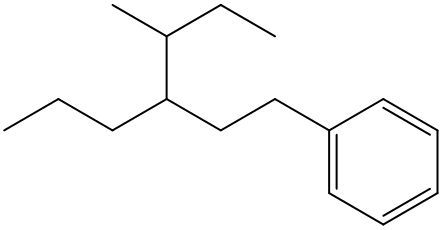
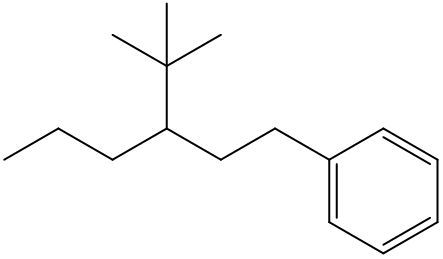
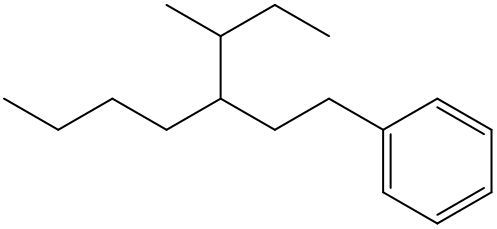
An alkyl halide consists of an alkyl group bonded to a halogen atom. In organic chemistry, halogens such as fluorine, chlorine, bromine, and iodine are treated as substituents on a carbon chain. When naming these compounds, the halogens are designated with specific prefixes: fluorine is referred to as fluoro, chlorine as chloro, bromine as bromo, and iodine as iodo.
When naming an organic compound, it is essential to identify the parent chain, which can vary in structure, such as being a six-membered chain or cyclic. The numerical location of the halogen substituents must be indicated in relation to the parent chain. This systematic approach to naming ensures clarity in identifying the structure and composition of alkyl halides, highlighting the importance of recognizing halogens as substituents within organic compounds.