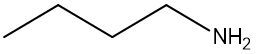
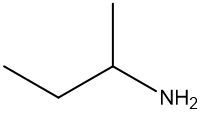
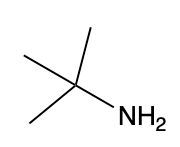
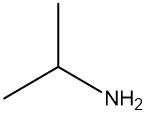
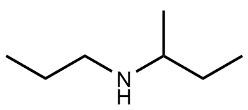
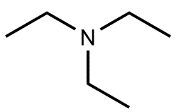
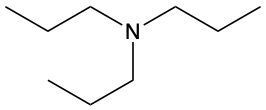
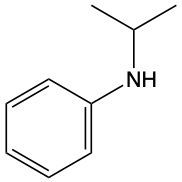
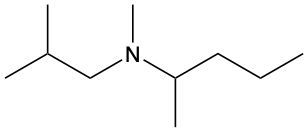
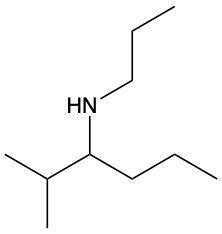
Amines are organic compounds characterized by the presence of one or more alkyl groups attached to a nitrogen atom. The naming of amines follows a specific system that is essential for proper identification and communication in chemistry. When naming amines, the substituents connected to the nitrogen atom form the initial part of the name, while the suffix "amine" is added to indicate the presence of the amine functional group.
For example, if a nitrogen atom is bonded to two ethyl groups and one methyl group, the compound would be named N,N-diethylmethylamine. Here, "N,N-diethyl" indicates the two ethyl groups attached to the nitrogen, and "methyl" refers to the additional methyl group, concluding with "amine" to signify the amine classification.
Understanding this naming convention is crucial for accurately describing amines in various chemical contexts, facilitating clearer communication among chemists and enhancing comprehension of organic compound structures.