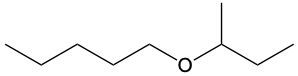
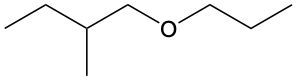
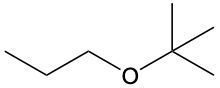
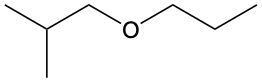
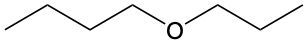
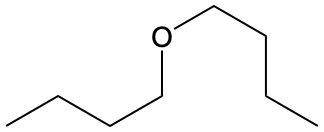
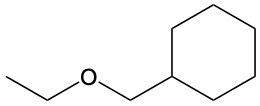
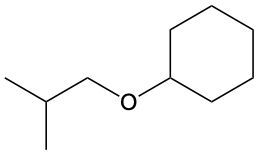
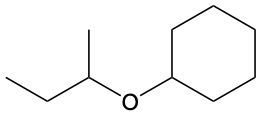
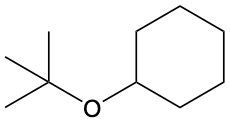
Ethers are organic compounds characterized by an oxygen atom bonded to two alkyl groups. This structure leads to a distinct naming convention that is essential for proper identification and communication in chemistry. The naming system for ethers involves identifying the two alkyl substituents attached to the oxygen atom. These substituents are named first, followed by the term "ether" to indicate the compound's classification.
To name an ether, one begins with the names of the two alkyl groups, which are listed in alphabetical order. For example, if the alkyl groups are ethyl and methyl, the compound would be named ethyl methyl ether. This systematic approach ensures clarity and consistency in naming ethers, making it easier to understand their structure and properties.
In summary, the key to naming ethers lies in recognizing the two alkyl groups and appending "ether" to their names, which reflects the unique bonding arrangement of these compounds.