Stoichiometry is essential for understanding the numerical relationships between compounds in a balanced chemical equation. When we introduce thermochemical equations, we focus on chemical reactions that involve the enthalpy of reaction, denoted as ΔHrxn. This value represents the heat change associated with the reaction and is crucial for calculating energy changes during chemical processes.
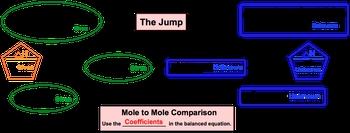
In thermochemical equations, we utilize a thermochemical stoichiometric chart, which allows us to relate the given quantity of one compound to the unknown quantity of another. The balanced chemical equation is accompanied by the ΔHrxn, and our goal is to connect this enthalpy value to various quantities such as moles, grams, or molecules involved in the reaction.
Unlike traditional stoichiometry, which often focuses on mole-to-mole comparisons, thermochemical equations emphasize the relationship between ΔH and moles. This distinction is vital, as it enables us to calculate the energy changes associated with specific amounts of reactants or products. Understanding this relationship is key to mastering thermochemical calculations and applying them effectively in various chemical contexts.