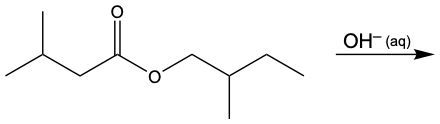
Saponification is a specific type of ester reaction where a hydroxide ion (OH-) in aqueous solution reacts with an ester. This reaction cleaves the ester bond, resulting in the formation of a carboxylate anion and an alcohol. The carboxylate anion is essentially the conjugate base of a carboxylic acid, which means it is formed when a hydrogen ion (H+) is removed from the acid.
In the saponification process, the ester linkage is broken by the hydroxide ion. This cleavage leads to the oxygen atom of the alcohol gaining a hydrogen atom (H), while the carbonyl carbon of the ester becomes negatively charged, resulting in the formation of the carboxylate anion. The overall reaction can be summarized as follows:
RCOOR' + OH- → RCOO- + R'OH
Here, RCOOR' represents the ester, RCOO- is the carboxylate anion, and R'OH is the alcohol produced. Understanding this reaction is crucial, as it is the reverse of esterification, where an alcohol and a carboxylic acid combine to form an ester. In summary, saponification is an important reaction in organic chemistry, particularly in the production of soaps and other surfactants.