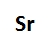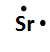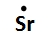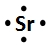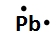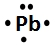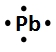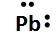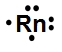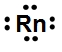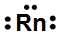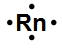Lewis dot symbols, also known as electron dot diagrams, are visual representations that illustrate the valence electrons of an atom or ion. Understanding valence electrons is crucial for predicting how atoms will bond and interact in chemical reactions. Valence electrons are the outermost electrons that participate in bonding, and their configuration varies between main group elements and transition metals.
For main group elements, which are found in groups 1A to 8A of the periodic table, the number of valence electrons corresponds directly to the group number. For instance, aluminum, located in group 3A, possesses three valence electrons. This straightforward relationship allows for easy identification of valence electrons in main group elements.
In contrast, transition metals exhibit a more complex arrangement. The number of valence electrons for these elements is determined by the sum of their s and d electrons. This means that when analyzing a transition metal, one must consider both the outermost s orbital and the d orbitals that are being filled. Recognizing whether an element is a main group element or a transition metal is essential for accurately determining its valence electron count.