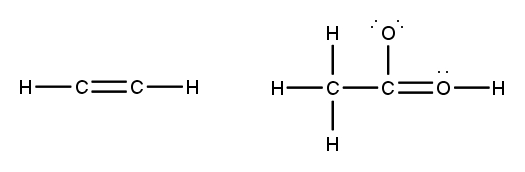
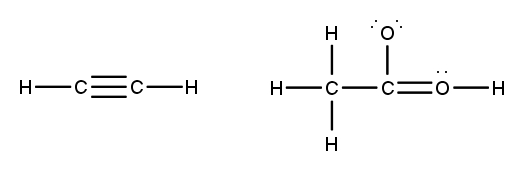
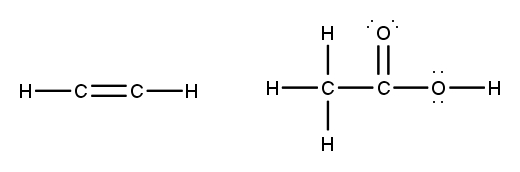
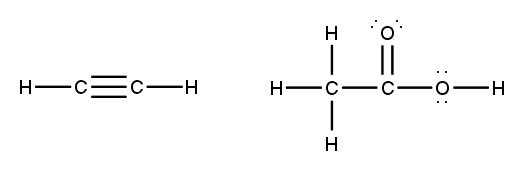
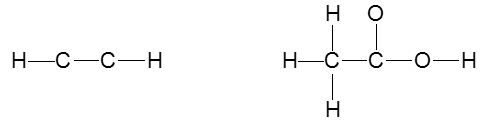To accurately draw a Lewis structure, it's essential to understand the role of multiple bonds between elements. These bonds can be categorized as single, double, or triple bonds, each differing in bond length and the number of shared electrons. As the bond type increases from single to triple, the bond length decreases: single bonds are the longest, while triple bonds are the shortest.
Each covalent bond consists of two electrons. In a single bond, two valence electrons are shared between two atoms, representing one electron pair. For a double bond, there are two bonds, leading to a total of four valence electrons shared, which corresponds to two electron pairs. In the case of a triple bond, three bonds are formed, resulting in six valence electrons being shared, equating to three electron pairs. Understanding these relationships is crucial for constructing accurate Lewis structures and predicting molecular behavior.