12. Liquids, Solids, and Intermolecular Forces
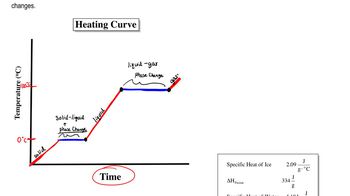
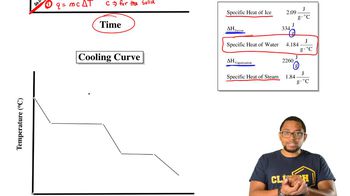
Heating and Cooling Curves
12. Liquids, Solids, and Intermolecular Forces
Heating and Cooling Curves
Practice this topic
- Multiple Choice
If 53.2kJ of heat are added to a 15.5g ice cube at - 5.00 oC, what will be the resulting state and temperature of the substance?
- Open QuestionAssume that you have a sample of gas at 350 K in a sealed container, as represented in part (a). Which of the drawings (b)–(d) represents the gas after the temperature is lowered from 350 K to 150 K and if the gas has a boiling point of 200 K? Which drawing represents the gas at 150 K if the gas has a boiling point of 100 K?
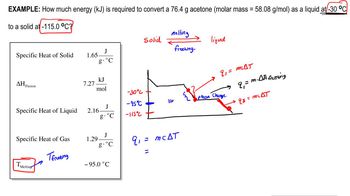
- Open QuestionUsing the values for the heat of fusion, specific heat of water, and/or heat of vaporization, calculate the amount of heat energy in each of the following:c. kilojoules needed to melt 24.0 g of ice at 0 °C, warm the liquid to 100 °C, and change it to steam at 100 °C
- Open QuestionWhat is a liquid's heat of vaporization?