Multiple Choice
Which of the following options is not an assumption made in deriving the Michaelis-Menten equation?
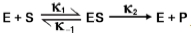
 Verified step by step guidance
Verified step by step guidance
 4:06m
4:06mMaster Michaelis-Menten Assumptions with a bite sized video explanation from Jason
Start learning
