Both α-keratin and tropocollagen have helical secondary structure. How do these molecules differ in (a) amino acid composition and (b) three-dimensional structure?

Draw the structure of the following amino acids, dipeptides, and tripeptides at low pH (pH 1) and high pH (pH 14). At each pH, assume that all functional groups that might do so are ionized.
a. Val
 Verified step by step guidance
Verified step by step guidance
Verified video answer for a similar problem:
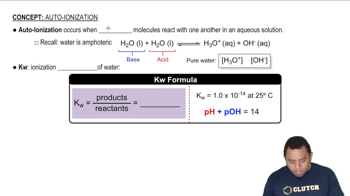
Key Concepts
Amino Acid Structure

Ionization at Different pH Levels
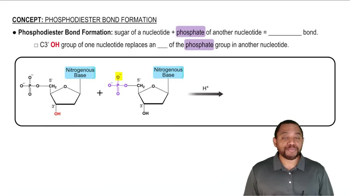
Peptide Bond Formation
Another endoprotease is trypsin. Trypsin hydrolyzes peptide bonds on the carboxyl side of lysine and arginine. If the following peptide sequence is hydrolyzed by trypsin, how many fragments will there be? Use the three-letter amino acid abbreviations to write the fragments out.
Ala-Phe-Lys-Cys-Gly-Asp-Arg-Leu-Leu-Phe-Gly-Ala
If the same peptide found in Problem 18.32 is subjected to acid hydrolysis, how many fragments will result? Why?
Ala-Phe-Lys-Cys-Gly-Asp-Arg-Leu-Leu-Phe-Gly-Ala
Draw the structure of the following amino acids, dipeptides, and tripeptides at low pH (pH 1) and high pH (pH 14). At each pH, assume that all functional groups that might do so are ionized.
d. Glu-Asp
Draw the structure of the following amino acids, dipeptides, and tripeptides at low pH (pH 1) and high pH (pH 14). At each pH, assume that all functional groups that might do so are ionized.
e. Gln-Ala-Asn
Interactions of amino acids on the interior of proteins are key to the shapes of proteins. In group (a), which pairs of amino acids form hydrophobic interactions? In group (b), which pairs form ionic interactions? Which pairs in group (c) form hydrogen bonds?
a. 1 Pro . . . Phe
2 Lys . . . Ser
3 Thr . . . Leu
4 Ala . . . Gly
