Back
BackProblem 1
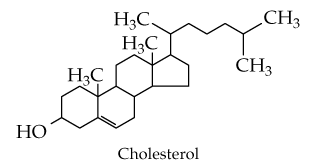
Cholesterol and cholate are sterols with very similar structures. However, the roles they play in the body are different: Cholate is an emulsifier, whereas cholesterol plays an important role in membrane structure. Identify the small differences in their structures that make them well suited to their jobs in the body. Given their similar structures, can the roles of these molecules be reversed?
Problem 3
How are long-chain fatty acids released from triacylglycerides transported through the bloodstream?
Problem 5a
How many molecules of acetyl-CoA are produced by catabolism of the following fatty acids, and how many β oxidations are needed?
a. Palmitic acid, CH3(CH2)14COOH
Problem 6
Look back at the reactions of the citric acid cycle (Figure 21.8) and identify the three reactions in that cycle that are similar to the first three reactions of the β oxidation of a fatty acid.
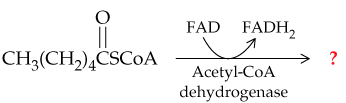
<IMAGE>
Problem 8
Which of the following classifications apply to the formation of 3-hydroxybutyrate from acetoacetate?
a. Condensation
b. Hydrolysis
c. Oxidation
d. Reduction
Problem 9c
Consider the reactions of ketogenesis.
c. What is the essential role of ketone bodies during prolonged starvation?
Problem 10
Starting with acetyl-S-enzyme-1 and malonyl-CoA, how many molecules of acetyl-CoA are needed to synthesize an 18-carbon fatty acid (C18:0)? How many molecules of CO2 are released in this process?
Problem 11
Oxygen is not a reactant in the β oxidation of fatty acids. Can β oxidation occur under anaerobic conditions? Explain.
Problem 12a
Identify each lipoprotein described here as either chylomicron, HDL, LDL, or VLDL.
a. Which lipoprotein has the lowest density? Why?
Problem 12d
Identify each lipoprotein described here as either chylomicron, HDL, LDL, or VLDL.
d. Which lipoprotein contains “bad cholesterol” from a vascular disease risk standpoint?
Problem 14
One strategy used in many different biochemical pathways is an initial investment of energy early on and a large payoff in energy at the end of the pathway. How is this strategy utilized in the catabolism of fats?
Problem 18
Compare the differences between β oxidation and fatty acid synthesis (lipogenesis). Are these pathways the reverse of each other?
Problem 19
Why do lipids make you feel full for a long time after a meal?
Problem 21
What is the purpose of bile acids in lipid digestion?
Problem 23
Write the equation for the hydrolysis of a triacylglycerol composed of stearic acid, oleic acid, and linoleic acid by pancreatic lipase.
Problem 26
What is the origin of the triacylglycerols transported by very low-density lipoproteins?
Problem 28
How is cholesterol transported around the body? When it leaves the liver, what is its destination and use?
Problem 29
The glycerol derived from lipolysis of triacylglycerols is converted into glyceraldehyde 3-phosphate, which then enters into step 6 of the glycolysis pathway. What further transformations are necessary to convert glyceraldehyde 3-phosphate into pyruvate?
Problem 32
How many molecules of acetyl-CoA result from catabolism of 1 molecule of glyceryl trilaurate?
Problem 39
Why is the stepwise oxidation of fatty acids called β oxidation?
Problem 44
How many moles of ATP are produced by the complete oxidation of 1 mol of myristic acid?
Problem 45
Arrange these following four molecules in increasing order of their biological energy content (per mole):
a. Sucrose
b. Myristic acid, CH3(CH2)12COOH
c. Glucose
d. Capric acid, CH3(CH2)8COOH
Problem 47a
Show the products of each step in the fatty acid oxidation of hexanoic acid.
a.
Problem 48
Write the equation for the final step in the catabolism of any fatty acid with an even number of carbons.
Problem 49a
How many molecules of acetyl-CoA result from complete catabolism of the following compounds?
a. Myristic acid, CH3(CH2)12COOH
Problem 53
What causes acetone to be present in the breath of someone with uncontrolled diabetes?
Problem 58
Name the starting material for fatty acid synthesis.
Problem 60
How many rounds of the lipogenesis cycle are needed to synthesize stearic acid, C17H35COOH?
Problem 64
Consuming too many carbohydrates causes deposition of fats in adipose tissue. How does this happen?
Problem 65
Why are extra calories consumed as carbohydrates stored as fat and not as glycogen?