Back
BackProblem 3a
The cofactors NAD+, Cu2+, Zn2+, coenzyme A, FAD, and Ni2+ are all needed by your body for enzymatic reactions.
a. Which cofactors are coenzymes?
Problem 4b
Describe the reactions that you would expect these enzymes to catalyze.
b. Aspartate transaminase
Problem 5a
Name the enzyme whose substrate is
a. Urea
Problem 7
Identify and describe the chemical change in the lyase-catalyzed reaction in Table 19.4 that involves fumarate and malate. Identify the substrate(s) and product(s).
Problem 8
Which of the following reactions can be catalyzed by a decarboxylase?
a.
b.
Problem 10
What do we mean when we say an enzyme is saturated with substrate? When an enzyme is saturated with substrate, how does adding more (a) substrate and (b) enzyme affect the rate of the reaction?
Problem 14
What kind of reaction product might be a competitive inhibitor for the enzyme that catalyzes its formation?
Problem 16
Which type of enzyme regulation is best for the following situations?
a. An enzyme that becomes overactive during a disease
b. An enzyme needed only when there is low blood glucose
c. An enzyme that springs into action when a traumatic injury occurs
d. An enzyme needed only during adolescence
Problem 17c
Does the enzyme described in each of the following statements require a cofactor to be active?
c. The presence of K+ does not affect the reaction.
Problem 18b
Which vitamin provides us with each of the following?
b. Coenzyme A
Problem 19
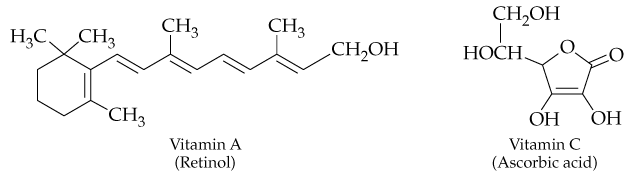
Compare the structures of vitamin A and vitamin C. Which one is water-soluble and which is fat-soluble? What structural features does each have that make one water-soluble and the other fat-soluble?
Problem 20
Based on the structure shown for retinol (vitamin A) and the names of the two related forms of vitamin A, retinal and retinoic acid, what do you expect to be the structural differences among these three compounds?
Problem 21
Vitamins are a diverse group of compounds that must be present in the diet. List four functions of vitamins in the body.
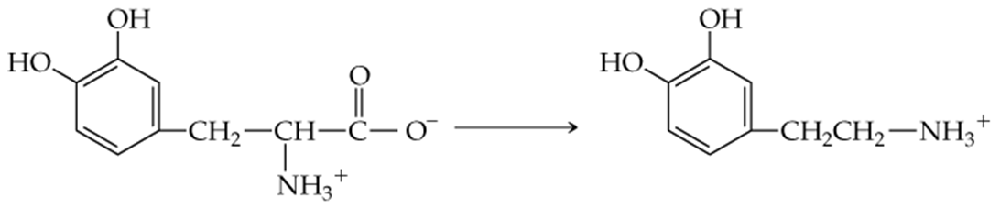
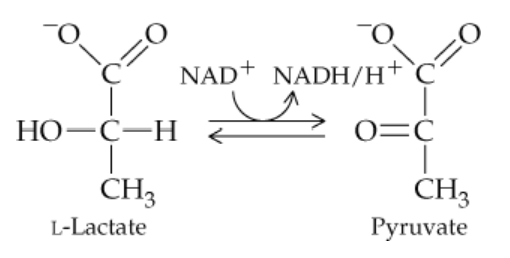
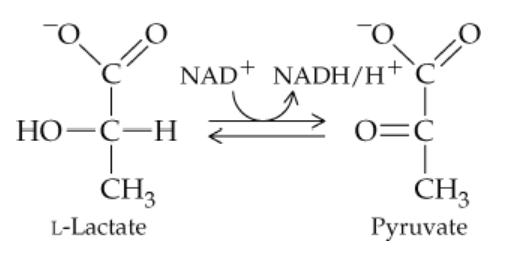
Problem 25a
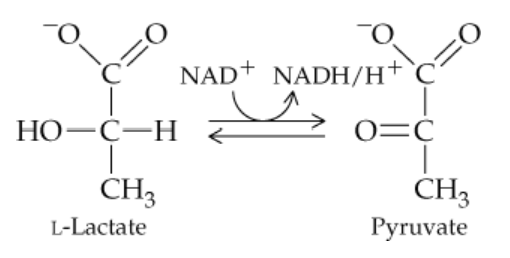
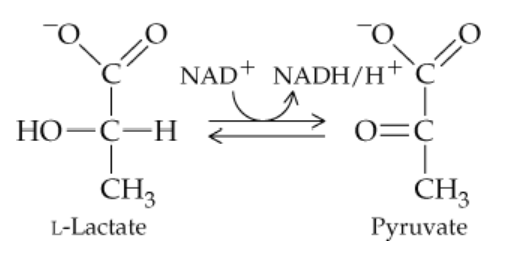
Answer questions (a)–(e) concerning the following reaction:
a. The enzyme involved in this reaction belongs to what class of enzymes?
Problem 25b
Answer questions (a)–(e) concerning the following reaction:
b. Since hydrogens are removed, the enzyme belongs to what subclass of the enzyme class from part (a)?
Problem 25c
Answer questions (a)–(e) concerning the following reaction:
c. What is the substrate for the reaction as written?
Problem 25d
Answer questions (a)–(e) concerning the following reaction:
d. What is the product for the reaction as written?
Problem 28a
Explain how the following changes affect the rate of an enzyme-catalyzed reaction in the presence of an uncompetitive inhibitor:
(a) increasing the substrate concentration at a constant inhibitor concentration
Problem 28b
Explain how the following changes affect the rate of an enzyme-catalyzed reaction in the presence of an uncompetitive inhibitor:
(b) decreasing the inhibitor concentration at a constant substrate concentration.
Problem 29b
Explain how the following mechanisms regulate enzyme activity.
b. Genetic control
Problem 30a
What type of enzyme regulation occurs in the following situations?
a. Buildup of the product of the pathway that converts glucose to pyruvate stops at the first enzyme in the multistep process.
Problem 30d
What type of enzyme regulation occurs in the following situations?
d. Conversion of isocitrate to α-ketoglutarate is inhibited by high levels of ATP. (Hint: ATP is neither a product nor a substrate in this reaction.)
Problem 32b
Name the vitamin to which each of these coenzymes is related.
b. Coenzyme A
Problem 33a
Which of the following is a cofactor and which is a coenzyme?
a. Cu2+
Problem 33b
Which of the following is a cofactor and which is a coenzyme?
b. Tetrahydrofolate
Problem 33c
Which of the following is a cofactor and which is a coenzyme?
c. NAD+
Problem 35a
Which of the following is a cofactor and which is a coenzyme?
a. Fe2+
Problem 35b
Which of the following is a cofactor and which is a coenzyme?
b. Pyridoxyl phosphate
Problem 36b
What general kinds of reactions do the following types of enzymes catalyze?
b. Decarboxylases
Problem 36c
What general kinds of reactions do the following types of enzymes catalyze?
c. Lipases