Back
BackProblem 1c
Name the following pathways:
c. Pathway for synthesis of glucose from lactate
Problem 4
Identify each step in glycolysis that is an isomerization.
Problem 6a
In Figure 22.3, compare the starting compound (glucose) and the final product (pyruvate).
a. Which is oxidized to a greater extent?
Problem 7
Use curved arrows (like those in Figure 22.3) to write an equation for the conversion of fructose to fructose 6-phosphate by ATP. At what step does fructose 6-phosphate enter glycolysis?
Problem 9a
In alcoholic fermentation, each mole of pyruvate is converted to one mole of carbon dioxide and one mole of ethanol. In the process, about 50 kcal/mol (209 kJ/mol) of energy is produced. Under the most favorable conditions, more than one-half of this energy is stored as ATP.
a. What happens to the remaining energy produced in alcoholic fermentation?
Problem 11
Pyruvate has three different fates. What are the three different molecules pyruvate is converted into? What conditions exist for the formation of each product?
Problem 12
Glycolysis of one molecule of glucose produces 8 ATP molecules. How many ATP molecules are produced from glycolysis of 10 glucose molecules?
Problem 19
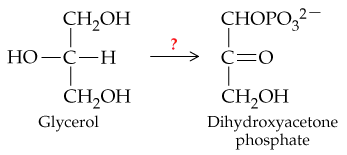
What two types of reactions convert glycerol to dihydroxyacetone phosphate?
Problem 20
What is the purpose of the Cori cycle?
Problem 23b
Glucose 6-phosphate is in a pivotal position in metabolism. Depending on conditions, glucose 6-phosphate follows one of several pathways. Under what conditions do the following occur?
b. Hydrolysis to free glucose
Problem 23d
Glucose 6-phosphate is in a pivotal position in metabolism. Depending on conditions, glucose 6-phosphate follows one of several pathways. Under what conditions do the following occur?
d. Glycogenesis
Problem 25b
Outline the conditions that direct pyruvate toward the following:
b. Conversion to ethanol and CO2
In what tissues or organisms is each pathway present?
Problem 25c
Outline the conditions that direct pyruvate toward the following:
c. Conversion to lactate
In what tissues or organisms is each pathway present?
Problem 25d
Outline the conditions that direct pyruvate toward the following:
d. Glucose synthesis (gluconeogenesis)
In what tissues or organisms is each pathway present?
Problem 28
Name the molecules used for gluconeogenesis. What are the sources of these molecules? Under what conditions would gluconeogenesis occur?
Problem 29
Fatty acids from stored triacylglycerols (fat) are not available for gluconeogenesis. Speculate why we do not have the enzymes to directly convert fatty acids into glucose. Plants (especially seeds) do have enzymes to convert fatty acids into carbohydrates. Why are they so lucky?
Problem 30b
The pathway that converts glucose to acetyl-CoA is often referred to as an “aerobic oxidation pathway.”
(b) Thinking back to Chapter 20, where does molecular oxygen enter the picture?
Problem 33
What are the major monosaccharide products produced by digestion of carbohydrates?
Problem 34
What are the products of digestion of proteins, triacylglycerols, maltose, sucrose, lactose, and starch?
Problem 36
What three products are formed from pyruvate under aerobic, anaerobic, and fermentation conditions?
Problem 39
What is the major purpose of the pentose phosphate pathway? What cofactor (coenzyme) is used?
Problem 42a
Which cells, liver, muscle, or brain, use the following pathways?
a. Glycolysis
Problem 42b
Which cells, liver, muscle, or brain, use the following pathways?
b. Gluconeogenesis
Problem 45a
Which glycolysis reactions are catalyzed by the following enzymes?
a. Pyruvate kinase
Problem 45d
Which glycolysis reactions are catalyzed by the following enzymes?
d. Phosphoglycerate mutase
Problem 46c
Review the 10 steps in glycolysis and then answer the following questions:
c. Which step is a dehydration?
Problem 47a
How many moles of ATP are produced by phosphorylation in the following?
a. Glycolysis of 1 mol of glucose
Problem 47b
How many moles of ATP are produced by phosphorylation in the following?
b. Aerobic conversion of 1 mol of pyruvate to 1 mol of acetyl-CoA
Problem 47c
How many moles of ATP are produced by phosphorylation in the following?
c. Catabolism of 1 mol of acetyl-CoA in the citric acid cycle
Problem 50
Lactate can be converted into pyruvate by the enzyme lactate dehydrogenase and the coenzyme NAD+. Write the reaction in the standard biochemical format, using a curved arrow to show the involvement of NAD+.