Back
BackProblem 2
CIA Problem 4.2 Draw the Lewis dot structures for the molecules CO and NO. What is different about these structures compared with the general examples we have seen so far? How could these Lewis structures provide insight into the high chemical reactivity of these molecules?
Problem 2a,b,c,d
How many covalent bonds are formed by each atom in the following molecules? Draw molecules using the electron-dot-symbols and lines to show the covalent bonds.
a. PH3
b. H2Se
c. HCl
d. SiF
Problem 3
What are likely formulas for the following molecules?
a. CH2Cl?
b. BH?
c. NI?
d. SiCl?
Problem 32
What is a coordinate covalent bond, and how does it differ from a covalent bond?
Problem 34d
Identify the bonds formed between the following pairs of atoms as either covalent or ionic.
d. Zinc and fluorine
Problem 35
Write electron-dot symbols to show the number of covalent bonds and the lone pairs of electrons in the molecules that are formed by reactions between the atoms in Problem 4.34.
a. Aluminum and bromine
b. Carbon and fluorine
c. Cesium and iodine
d. Zinc and fluorine
e. Lithium and chlorine
Problem 38
Which of the following contains a coordinate covalent bond? (Hint: How many covalent bonds would you expect the central atom (underlined/bold) to form?)
a. PbCl2
b. Cu(NH3)42+
c. NH4+
Problem 41
A compound of gallium with chlorine has a melting point of 77°C and a boiling point of 201°C. Is the compound ionic or covalent? What is a likely formula?
Problem 44b
Distinguish between the following:
b. A structural formula and a condensed structure
Problem 44c
Distinguish between the following:
c. A lone pair and a shared pair of electrons
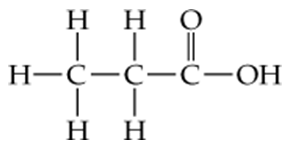
Problem 49a
Consider the following possible structural formulas for C3H6O2. If a structure is not reasonable, explain what changes could be made to convert it to a reasonable structure.
a.
Problem 53c
Expand the following condensed structures into the correct structural formulas.
c. CH3CH2OCH2Cl
Problem 55e
Draw a Lewis structure for the following molecules:
e. BeCl2 (Note: This molecule does not follow the octet rule.)
Problem 62b
Draw a Lewis structure for the following polyatomic ions:
b. Sulfite, SO32–
Problem 65a
Sketch the three-dimensional shape of the following molecules:
a. Methylamine, CH3NH2
Problem 75b
Based on electronegativity differences, would you expect bonds between the following pairs of atoms to be largely ionic or largely covalent?
b. Ca and Cl
Problem 85a
The discovery in the 1960s that xenon and fluorine react to form a molecular compound was a surprise to most chemists, because it had been thought that noble gases could not form bonds.
a. Why was it thought that noble gases could not form bonds?
Problem 88d
The following formulas are unlikely to be correct. What is wrong with each?
d. C2OS
Problem 89a
Which of the following compounds contain ionic bonds? Which contain covalent bonds? Which contain coordinate covalent bonds? (A compound may contain more than one type of bond.)
a. BaCl2
Problem 90b
The phosphonium ion, PH4+ is formed by reaction of phosphine, PH3, with an acid.
b. Predict its molecular geometry.
Problem 90d
The phosphonium ion, PH4+ is formed by reaction of phosphine, PH3, with an acid.
d. Explain why the ion has a +1 charge.
Problem 93
The sulfite ion (SO32–) and sulfur trioxide (SO3) have the same chemical formulas but different molecular geometries. Draw the Lewis dot structures and identify the molecular geometry of each.
Problem 100(iv)
Which of the following elements would you expect to form (iv) both covalent and ionic bonds? (More than one answer may apply; remember that some nonmetals can form ionic bonds with metals.) Explain your answers.
a. Oxygen
b. Potassium
c. Phosphorus
d. Iodine
e. Hydrogen
f. Cesium