Back
BackProblem 1
Alcohol dehydrogenase, found in liver cells, converts ethanol into acetaldehyde. What type of protein is alcohol dehydrogenase?
Problem 2
Cortisol levels rise under stressful conditions. Oxytocin can induce relaxation and romantic feelings. What type of protein are cortisol and oxytocin?
Problem 3
Consult Table 18.3 and draw alanine. Label the functional groups and give the three-letter abbreviation and the one-letter abbreviation. What group does the side chain fall into?
Problem 4
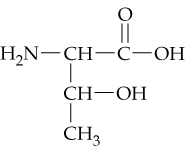
Examine the ball-and-stick model of valine below. Identify the carboxyl group, the amino group, and the R group.
<IMAGE>
Problem 5a
Indicate whether each of the following molecules is an α-amino acid or not, and explain why.
a.
Problem 6
Using Table 18.3, name the α-amino acids that (a) contain an aromatic ring, (b) contain sulfur, (c) are alcohols, and (d) have alkyl-group side chains.
Problem 7
Valine is an amino acid with a nonpolar side chain and serine is one with a polar side chain. Draw the two amino acids.
a. Why is the side chain for valine nonpolar, whereas the side chain for serine is polar?
Problem 8
Which amino acid is hydrophilic (dissolves in aqueous solutions)? Why?
a. isoleucine
b. phenylalanine
c. aspartic acid
Problem 10
Is serine chiral? Draw serine and identify the chiral atom. Explain why serine is chiral.
Problem 12
Two of the 20 common amino acids have two chiral carbon atoms in their structures. Identify these amino acids and their chiral carbon atoms.
Problem 13
Draw the structure of glutamic acid at low pH, at high pH, and at the two forms that exist between low pH and high pH. Which of these structures represents the zwitterion?
Problem 15
Valine is an amino acid with a nonpolar side chain, and serine is an amino acid with a polar side chain. Draw the two dipeptides that can be formed by these two amino acids. Identify the peptide bond.
Problem 16a
Tripeptides are composed of three amino acids linked by peptide bonds. Given a set of amino acids, you can make several different tripeptides.
a. Use the three-letter shorthand notations to name all the tripeptides that can be made from serine, tyrosine, and glycine. Each amino acid will be used once in each tripeptide.
Problem 17
Using three-letter abbreviations, show the six tripeptides that contain isoleucine, arginine, and valine.
Problem 18a
Identify the amino acids in the following dipeptide and tripeptide, and write the abbreviated forms of the peptide names. Copy the dipeptides, draw a box around the peptide bonds, and use an arrow to identify the α-carbon atoms. Draw a circle around the R groups, and indicate if the R groups are neutral, polar, acidic, or basic.
a.
Problem 19
There are eight amino acids in vasopressin. How many peptide bonds are in this small protein?
Problem 20a
What atoms are present in a planar unit in a protein chain?
Problem 20b
How many amino acid units do these atoms come from? Why are these units planar?
Problem 21
How many ways can four different amino acids be arranged in a peptide so that each peptide is unique?
Problem 23
Examine the α-helix in Figure 18.1 and determine how many backbone C and N atoms are included in the loop between an amide hydrogen atom and the carbonyl oxygen to which it is hydrogen bonded.
Problem 24
Consult the β-sheet in Figure 18.2 and (a) name the bonding responsible for the sheet formation and (b) identify the specific atoms responsible for this bonding.
Problem 25a
Complete the following two sentences with either globular or fibrous:
a. Proteins with secondary structure composed primarily of alpha-helix are___________ proteins.
Problem 30a
For each of the conjugated proteins described, identify to which class of conjugated protein it belongs.
a. Cholesterol is attached to this protein in order to move through the blood system.
Problem 30b
For each of the conjugated proteins described, identify to which class of conjugated protein it belongs.
b. Ionized zinc is attached to this protein so the protein can function.
Problem 30c
For each of the conjugated proteins described, identify to which class of conjugated protein it belongs.
c. Phosphate groups are attached to this protein.
Problem 31
Both α-keratin and tropocollagen have helical secondary structure. How do these molecules differ in (a) amino acid composition and (b) three-dimensional structure?
Problem 32
Another endoprotease is trypsin. Trypsin hydrolyzes peptide bonds on the carboxyl side of lysine and arginine. If the following peptide sequence is hydrolyzed by trypsin, how many fragments will there be? Use the three-letter amino acid abbreviations to write the fragments out.
Ala-Phe-Lys-Cys-Gly-Asp-Arg-Leu-Leu-Phe-Gly-Ala
Problem 33
If the same peptide found in Problem 18.32 is subjected to acid hydrolysis, how many fragments will result? Why?
Ala-Phe-Lys-Cys-Gly-Asp-Arg-Leu-Leu-Phe-Gly-Ala
Problem 34a
Draw the structure of the following amino acids, dipeptides, and tripeptides at low pH (pH 1) and high pH (pH 14). At each pH, assume that all functional groups that might do so are ionized.
a. Val
Problem 34d
Draw the structure of the following amino acids, dipeptides, and tripeptides at low pH (pH 1) and high pH (pH 14). At each pH, assume that all functional groups that might do so are ionized.
d. Glu-Asp