Draw the structures of the following compounds and use dashed lines to indicate where they form hydrogen bonds to other molecules of the same kind: (ii) methyl formate

Draw the structures of the following compounds and use dashed lines to indicate where they form hydrogen bonds to other molecules of the same kind: (i) formic acid
 Verified step by step guidance
Verified step by step guidance
Verified video answer for a similar problem:
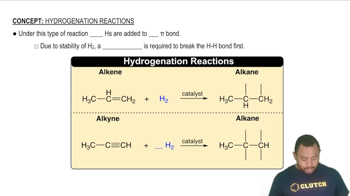
Key Concepts
Hydrogen Bonding
Molecular Structure of Formic Acid
Dashed Lines in Molecular Diagrams
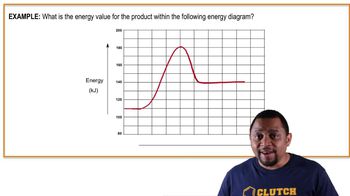
Consider the following unnatural amino acid:
a. If two molecules react to form an ester, what is the structure of the ester product?
Consider the following unnatural amino acid:
c. Draw the cyclic ester resulting from the intramolecular reaction of the hydroxyl group of this amino acid with its carboxyl group (cyclic esters are called lactones).
Arrange these compounds in order of increasing boiling points and explain your rationale for the order.
(i) formic acid
(ii) methyl formate
(iii) formamide.
Write the equation for the ionization of hexanoic acid in water at pH 7.4.
Suppose you have a sample of benzoic acid dissolved in water.
b. Now assume that aqueous NaOH is added to the benzoic acid solution until pH 12 is reached. Draw the structure of the major organic species present.
