Name the following compounds:
a.

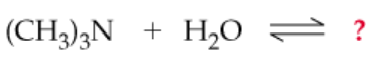
 Verified step by step guidance
Verified step by step guidance
Name the following compounds:
a.
Complete the following equations (Hint: Answers may include concepts learned from previous organic chapters):
a.
Complete the following equations (Hint: Answers may include concepts learned from previous organic chapters):
c.
Baeocystin is a hallucinogenic compound that is isolated from the mushroom Psilocybe baeocystis and has the structure shown below. What heterocyclic base (Table 16.1) is the parent of this compound?
Benzene and pyridine are both single-ring, aromatic compounds. Benzene is a neutral compound that is insoluble in water. Pyridine, with a similar molar mass, is basic and completely miscible with water. Explain these phenomena.
Lemon juice, which contains citric acid, is traditionally recommended for removing the odor associated with cleaning fish. What functional group is responsible for a 'fishy' odor, and why does lemon juice work to remove the odor? If possible, test this at home using a piece of fish.